Showing posts with label melasma. Show all posts
Showing posts with label melasma. Show all posts
Tuesday, February 7, 2017
How to Lighten Hyperpigmentation, Dark Spots and Sun Spots
Topical Treatments/Skin Lighteners:
Wednesday, August 12, 2015
How to Treat Melasma
Melasma is a difficult form of hyperpigmentation treat. The factors that trigger melasma, such as hormones, sun exposure and genetics, are a part of life and as such, difficult to control. Once melasma is triggered, the smallest amount of UV exposure or hormonal change is enough to cause melasma to darken, or even return after successful treatment.
Due to it's stubborn nature, Melasma is treated slightly differently than hyperpigmentation from sun damage or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. The three types of melasma (dermal, epidermal and mixed) all respond to treatment differently.
The three factors in treating all melasma cases are:
Skin Lightening Creams - The most effective treatments for melasma are lightening, or bleaching creams. Lightening creams, or bleaching creams work to increase cell turnover and inhibit melanin production. When using lightening creams, the skin will peel and start to slough of the dead skin for a brighter, more even skin tone. One of the most effective lightening agents is hydroquinone, a bleaching agent that is available at concentrations up to 2% over the counter and concentrations much higher with prescription. Hydroquinone doesn't actually bleach the skin, but slows down or stops the overproduction of melanin. Other effective lightening agents are Azelaic acid, Kojic Acid, Alpha Hydroxy Acids, and Tretinoin. For more information on Skin Lightening Creams & Treatment visit here.
Other treatment options include exfoliation. Both physical and chemical exfoliation can help reduce the appearance of melasma. Microdermabrasion and chemical peels both exfoliate the skin to increase cell turnover and speed the transit of dark pigmentation out of the skin. Chemical peels initiate the process of removing the first few layers of skin - improving overall texture and skin clarity while helping lift dark patches in the skin. Exfoliation also helps prep the skin for skin lightening treatments and allows products to absorb better. Microdermabrasion and chemical peels must be performed by a professional. If the skin reacts poorly to treatment, the melasma could darken.
Sun Protection - As with all skin lightening treatments, diligent sun protection use is a must. Sun exposure will cause melasma to worsen and cause faded cases of melasma to return. This is because melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigmentation, are stimulated by even the smallest amount of UV exposure. This is why melasma often gets worse during the summer, and why people tend to have recurring cases of melasma. Skin lighteners can also increase skin sensitivity and cause it to burn more easily. Sun protection is necessary to start the fading process and to keep the melasma from returning.
Time - Melasma treatment requires commitment. Sun protection and lightening products need to be used faithfully to see results. Melasma pigmentation forms gradually and it fades as such, so it may take months to completely fade. It's important not to over-treat melasma or cause unnecessary irritation, as inflammation can stimulate melanin production and worsen the existing melasma.
Melasma can be difficult to treat because the discoloration is generally caused by a underlying hormonal imbalance. Without treating the imbalance, the pigmentation will keep returning. In some cases, melasma will fade on its own - generally after the hormonal imbalance has been restored. For example, pregnancy induced melasma generally clears up several months after delivery.
Due to it's stubborn nature, Melasma is treated slightly differently than hyperpigmentation from sun damage or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. The three types of melasma (dermal, epidermal and mixed) all respond to treatment differently.
The three factors in treating all melasma cases are:
- The right professional treatment option, ie: laser, Ipl Photofacial
•Skin Lightening Creams
•Sun Protection
•Time
Other treatment options include exfoliation. Both physical and chemical exfoliation can help reduce the appearance of melasma. Microdermabrasion and chemical peels both exfoliate the skin to increase cell turnover and speed the transit of dark pigmentation out of the skin. Chemical peels initiate the process of removing the first few layers of skin - improving overall texture and skin clarity while helping lift dark patches in the skin. Exfoliation also helps prep the skin for skin lightening treatments and allows products to absorb better. Microdermabrasion and chemical peels must be performed by a professional. If the skin reacts poorly to treatment, the melasma could darken.
Sun Protection - As with all skin lightening treatments, diligent sun protection use is a must. Sun exposure will cause melasma to worsen and cause faded cases of melasma to return. This is because melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigmentation, are stimulated by even the smallest amount of UV exposure. This is why melasma often gets worse during the summer, and why people tend to have recurring cases of melasma. Skin lighteners can also increase skin sensitivity and cause it to burn more easily. Sun protection is necessary to start the fading process and to keep the melasma from returning.
Time - Melasma treatment requires commitment. Sun protection and lightening products need to be used faithfully to see results. Melasma pigmentation forms gradually and it fades as such, so it may take months to completely fade. It's important not to over-treat melasma or cause unnecessary irritation, as inflammation can stimulate melanin production and worsen the existing melasma.
Melasma can be difficult to treat because the discoloration is generally caused by a underlying hormonal imbalance. Without treating the imbalance, the pigmentation will keep returning. In some cases, melasma will fade on its own - generally after the hormonal imbalance has been restored. For example, pregnancy induced melasma generally clears up several months after delivery.
Labels:
beauty,
chemical peels,
dark spots,
exfoliatation,
health,
hyperpigmentation,
melanin,
melasma,
microdermabrasion,
skin care,
skin lightening,
sun damage,
sun protection,
sunscreen,
UV light
Saturday, July 11, 2015
What causes Acne Scars, Dark Spots and Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation?
If you have ever struggled with acne, you'll probably be familiar with those dark marks that linger for months after your acne has healed - These spots are called post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation is the result of any inflammatory skin reaction from acne, dermatitis, psoriasis, skin infections, skin trauma, burns and drug eruptions. PIH from acne and other skin issues are made worse by picking or squeezing, and sun exposure.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is characterized by a flat area of discoloration of the site of injury. This coloration can range from pink, red, purple brown or black - depending on the tone and depth of your skin. The severity of the injury or acne legion also correlates to the darkness of pigmentation; the darker the spot, the longer it'll take to fade.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is very common in acne prone skin as well as deeper skin tones. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is often referred to as acne scars, however these spots are not true scars. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation doesn't involve changes to collagen in the skin, so there is no actual scar tissue.
Although post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation generally fades on its own, treatments such as laser genesis, lightening creams, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and daily sun protection can help speed up the fading process.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation is the result of any inflammatory skin reaction from acne, dermatitis, psoriasis, skin infections, skin trauma, burns and drug eruptions. PIH from acne and other skin issues are made worse by picking or squeezing, and sun exposure.
 |
| source |
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation occurs when acne, or any other injury causes the skin to be inflamed. This inflammation triggers excess melanin production, leaving behind discoloration after the injury or acne has healed. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation will fade over time, however it can take up to two years to completely go away.
 |
| source |
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is very common in acne prone skin as well as deeper skin tones. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is often referred to as acne scars, however these spots are not true scars. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation doesn't involve changes to collagen in the skin, so there is no actual scar tissue.
Although post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation generally fades on its own, treatments such as laser genesis, lightening creams, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and daily sun protection can help speed up the fading process.
Saturday, June 13, 2015
What causes Melasma, Hyperpigmentation or Dark Spots?
Hyperpigmentation, or dark spots, can be triggered by several different factors. While sun exposure is a major cause, other issues like hormonal changes and acne can lead to hyperpigmentation.
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation that is linked to hormonal changes. Melasma is characterized by dark, irregular discoloration ranging in size from freckles to large patches. These dark spots are usually found on the upper cheeks, upper lip, forehead and nose. Melasma very common in pregnant women, in fact its often called ‘the mask of pregnancy.”
Hormone shifts triggered by birth control pills, pregnancy, thyroid conditions and menopause are the most common causes of melasma. Hormonal changes can cause melanin production to spike. Melasma is thought to occur when melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, are stimulated by female hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. This hormonal stimulation causes melanin to produce more pigments when exposed to sunlight.
Both men and women can develop melasma, however its much more common in women. Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing melasma. People with darker skin such as African, African American, Asian, Indian, Latin/Hispanic, Mediterranean and Middle Eastern descent are more prone to hyperpigmentation and melasma. This is because the melanocytes are more active in darker skin tones.
There are three types of melasma:
All cases of melasma start out in the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin. Dermal melasma occurs when the affected cells are inflamed or over irritated. Inflammation can cause a temporary split between the dermis and epidermis allowing cells from melasma drop from the epidermis into the dermis. Once in the dermis, melasma is very difficult to treat because the cells become resistant to topical treatments.
 |
| source |
Hormone shifts triggered by birth control pills, pregnancy, thyroid conditions and menopause are the most common causes of melasma. Hormonal changes can cause melanin production to spike. Melasma is thought to occur when melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, are stimulated by female hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. This hormonal stimulation causes melanin to produce more pigments when exposed to sunlight.
Both men and women can develop melasma, however its much more common in women. Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing melasma. People with darker skin such as African, African American, Asian, Indian, Latin/Hispanic, Mediterranean and Middle Eastern descent are more prone to hyperpigmentation and melasma. This is because the melanocytes are more active in darker skin tones.
- Epidermal melasma
- occurs in superficial layers of the skin
- well-defined borders
- typically dark brown in color
- responds very well to treatment
- Dermal melasma
- occurs in deeper layers of the skin
- undefined borders
- light brown or blueish in color
- Mixed melasma
- a combination of epidermal and dermal melasma
- most common type of melasma
- mix of light brown, dark brown and blueish in color
All cases of melasma start out in the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin. Dermal melasma occurs when the affected cells are inflamed or over irritated. Inflammation can cause a temporary split between the dermis and epidermis allowing cells from melasma drop from the epidermis into the dermis. Once in the dermis, melasma is very difficult to treat because the cells become resistant to topical treatments.
Friday, June 5, 2015
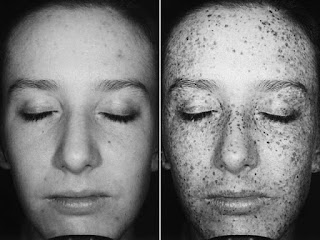
How Does Sun Damage Affect Your Skin?
Sun damage is the major cause of hyperpigmentation - even spots from melasma, post inflammatory or other damage is exacerbated by sun damage. In addition to hyper pigmentation sun damage can cause:
About 80% of a person's lifetime sun exposure is acquired by the age of 18 - but it's never too early or too late to take care your skin. A few things you can do to prevent sun damage are:
While prevention is always best, there are things you can do to help repair and correct damage from sun exposure. A few simple changes to your beauty routine and a day at the spa can help you turn back the clock.
Tips to help repair sun damage:
- Wrinkles
- Dry or rough textured skin
- Broken capillaries
- Freckles
- Macules or dark spots
- A weakening of the connective tissues of your face which reduces elasticity.
 |
| source |
About 80% of a person's lifetime sun exposure is acquired by the age of 18 - but it's never too early or too late to take care your skin. A few things you can do to prevent sun damage are:
- Wear a sunblock or sunscreen of at least SPF30 and diligently reapply every 2-3 hours
- Wear protective clothing, hats and sunglasses
- Choose make-up and skin care products with additional UV protection
- Limit your sun exposure at peak hours- 10 am to 2pm
Tips to help repair sun damage:
- Wear sunscreen! Consistent sunscreen use will prevent further damage and allow your skin to recover.
- Hydrate - Keep your body and your skin hydrated by drinking plenty of water and using a good moisturizer. Wrinkles and fine lines look deeper on dehydrated skin!
- Exfoliate - Chemical exfoliation dissolves and sloughs off dead, dull skin more evenly than a manual exfoliate like a loofah or scrubbing beads. Exfoliation will brighten the skin and prime it for any treatments you apply afterwards.
- Try spa treatments such as:
- Lightening treatments- skin lightening creams like hydroquinone and retinols can help lighten the dark spots and hyperpigmentation
- IPL Photo Facials - IPL photo facials help improve dark spots, broken capillaries, skin texture, wrinkles and other signs of sun damage
- High Frequency Technology - High Frequency treatments remove dark spots, broken capillaries, spider veins and other minor skin irregularities
Labels:
age spots,
anti-aging,
beauty,
dark spots,
health,
hyperpigmentation,
melanin,
melasma,
pih. post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation,
skin care,
sun damage,
sun protection,
sunscreen,
UV light
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)

