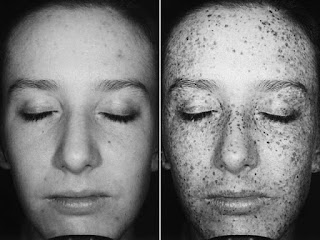
A major source dark spots, often called age spots, are caused from sun exposure not as a direct result of age. To make matters worse, sun damage is cumulative. The older you get, the more sun damage you accumulate. Sun damage can manifest on the skin 20-30 years down the line.
A major source dark spots, often called age spots, are caused from sun exposure not as a direct result of age. To make matters worse, sun damage is cumulative. The older you get, the more sun damage you accumulate. Sun damage can manifest on the skin 20-30 years down the line. We all know that excessive sun exposure is bad for your health - the 'healthy glow' people seek every summer contributes to the long-term damage of your skin. However, studies have proven that sun exposure also makes you look older. A 2006 study conducted by Proctor & Gamble showed that skin tone can affect a person's perceived age by as much as 20 years. Sun exposure causes photo-aging, the deterioration of the skin from harmful UV rays.
Sun exposure causes photo-aging, the deterioration of the skin from harmful UV rays. The effects of sun damage include:
- Dark Spots or a blotchy, mottled complexion
- Premature Lines and Wrinkles
- Telangiectasias, the dilation of blood vessels under the skin, or broken capillaries
- Elastosis, the deterioration of collagen and elastin that causes the skin to sag
- Thinning Skin and Changes in Skin Texture
- Pre-cancerous and cancerous skin lesions
When skin is exposed to UV light, melanin is produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. The production of melanin is the body's defense against sun damage - melanin is able to disperse about 99.9% of absorbed UV radiation. In some areas of the skin, the concentration of cells may vary - dense amounts of cells can create melanin “deposits,” causing dark spots. As we age, our cells become less diffuse and this defense mechanism becomes less effective, so dark spots become a more frequent occurrence.
Thankfully, there are ways to counteract the signs of aging caused by sun damage. Lightening creams, advanced skin care and Med Spa services such as IPL photo facials, microdermabrasion, chemical peels and high frequency treatments can help rejuvenate the skin.
Next, will discuss these treatments in depth and explain how they can help sun damaged skin. Until then, don't forget to wear your sun screen!